# Electrovalent Bonding
In similar manner by which polar **Water Molecule** unlike atoms (Hydrogen Atoms 78 / Oxygen Atom ID (210) of Figure (3-27) take-on opposite electrical Charges (B+ / B-), other gas-atoms molecule (s) experience the same **Electrical Charge Effect** (q - q') when covalent-electron sharing occurs, as illustrated in polar-molecule **Carbon Dioxide** CO2 (910) of Figure (9-2) as to allotropic molecule of **Ozone** 03 (930) of Figure (9-4).
(210) of Figure (3-27)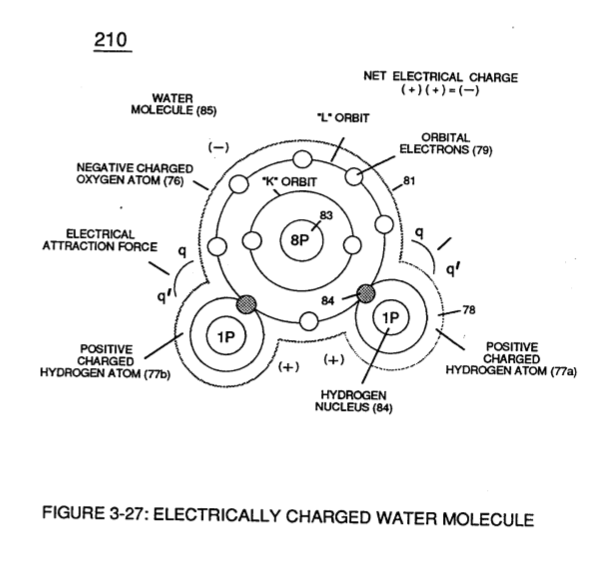
**Carbon Dioxide** molecule 0>2 (910) **Electrovalent Bonding** forces (q - q') comes into existence when unlike **Carbon Atom** (902) shares electrons with each of two **Oxygen Atoms** (901a / 901b) since the accepted and captured covalent electrons migrates toward both oxygen atom (901a and 901b) nucleus proton-cluster of eight particles having a greater total positive static charge than **Carbon Atom** (902) nucleus proton-cluster of only six ... forming polar charged (B+ / B- ) Carbon Dioxide CO2 molecule (910).
The additive two captured/accepted electrons (total ten 10 electrons as to only eight B protons) causes both oxygen atoms (901a / 90lb) to individually take-on a negative electrical charge (B-) while the center positioned **Carbon Atom** (902) emanates a positive electrical charge (B+) of equal but opposite electrical intensity (q - q') when its shared electrons is/are being used/accepted by unlike oxygen atoms (901a / 901b).
**N**[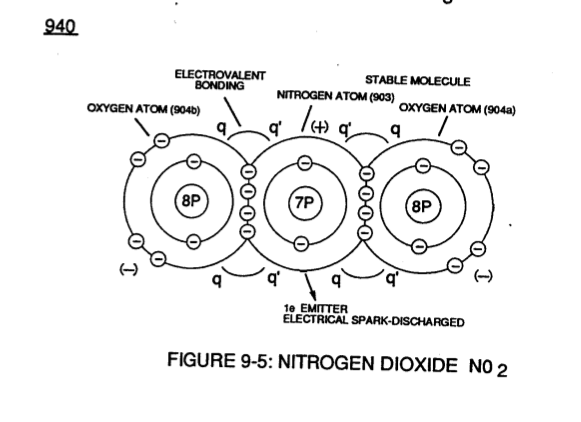](https://stanslegacy.com/uploads/images/gallery/2023-12/4jBBAH1Aek3P4fAq-image-1702959273104-14-27.png)**itrogen Dioxide** N02 (940) of Figure (9-5) is another example of polar electrical charging (q \_ q') of two unlike atoms forming a stable molecule wherein a **Nitrogen Atom** (N) (903) covalently interlocks with two **Oxygen Atoms** (904a / 904b).
Identical gas-atoms of **Oxygen Atoms** (905a / 905b 1905c) of Figure (9-4) further exhibits **Electrical Charging Effect** (q - q') since in all cases the second **Electron Shell** (L-orbit) can accept up to eight (8) electrons to cause molecule stabilization.
[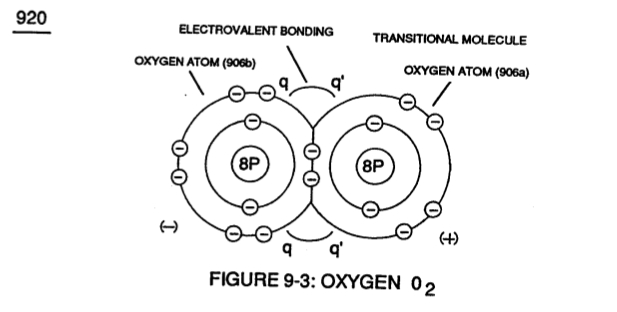](https://stanslegacy.com/uploads/images/gallery/2023-12/aQWJTdi70bs26CYM-image-1702959414837-16-51.png)Transitional gas-molecule of **Oxygen** 02 combines together two oxygen atoms (906a / 906b) in this way while allowing the donor oxygen atom (906b) to except another oxygen atom (905c) of Figure (9-4) since it's L-Orbit (Outer Shell) still has available two "**Electron-Gaps**" for covalent **Linkup**, as illustrated in (920) of Figure (9-3).
**Electrical Charging Effect** (q -g') is **Electrical Attraction Force** (q - q') of opposite electrical polarity between the established positive (B+) electrically charged atom (s) and the negative (B-) electrical charged atom (s).
Electrical intensity of **Opposite Electrical Attraction Force** (q-qa'- 907a + q-qb' - 907b) (herein after called **Electrovalent Bonding**) (total electrical bonding force between two opposite electrical charged atoms) are equivalent to the total number of electrons being used/accepted by the host atom (s) having the greater positive charged (B+) nucleus as so established under the laws of physics which states for "*every action there is an equal and opposite reaction*".
This is possible due the fact that all orbiting individual electrons display their own negative electrical charge (B-) whereas each proton-particle separately supports a positive electrical charge (B+)
... both opposite electrical charged particles (Proton as to each Electron) being equal in electrical magnitude (B+ / B-).
And due to the fact that the oxygen atom does not take-on an electromagnetic charged field since its electrons pair together and spin in opposite direction.