# Gyroscopic Spiking Effect
The gyroscopic spiking to cause an stable atom (*non-radioactive*) to start emitting nuclear radiation (*becoming radioactive*) generally occurs whenever the quiescent atom absorbs a predetermined amount of electromagnetic energy (*gamma rays*) from another source beyond the “**Energy Spectrum**” of the atom or whenever the atom excepts a foreign mass entity (s) such as additional and unwanted atomic particle (s) into its nucleus “**orbital gyroscopic architecture**”
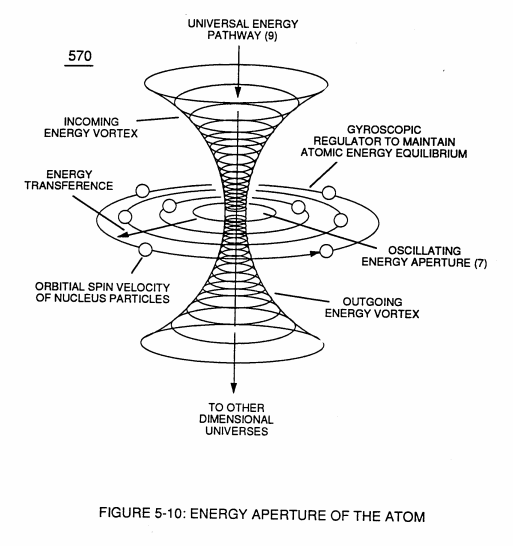
... herein, defined as being composed of orbiting spinning mass entities about an central axis and each electrical charged mass entity being displaced in space relationship to each other in a predetermined geometrical form by way of an emanating interlocking “**Electrical Bonding Forces**”(qq’), as so illustrated in WFC Figure (10-6) as to WFC Figure (5-10).
| [](https://stanslegacy.com/uploads/images/gallery/2024-03/chZtVg6MxmosCLOH-image-1709348095958.png)
|
Once absorbed into the **Energy Spectrum of the Atom**, the additive **Gamma Rays** of electromagnetic energy (*at an given elevated level of magnitude*) causes the orbiting spinning nuclear particles (orbital gyroscopic architecture) to deflect and be moved to another energy level somewhat different in geometrical form as previously arranged
... disrupting the **electrical bonding forces** (qq’) inside the atom nucleus to cause elliptical pathway of the orbiting nuclear particles away from circular symmetry
... superimposing an oscillatory electrical attraction force (RU-RU’ ~ ST’-ST) (pulsating) onto the nucleus “**Energy Aperture**” ... resulting in the combined altered and abnormal “**Condition of Changes**” which is hereinafter referred to as the “**Wobbling Effect**.”
The overall characteristic of the **Wobbling Effect** is that of having a reoccurring apogee and perigee nodes of elliptical movement about the centrally positioned **Energy Aperture** of the nucleus of the atom.