Avalanche Diodes
What is avalanche diode?
An avalanche diode is a special type of semiconductor device designed to operate in reverse breakdown region. Avalanche diodes are used as relief valves (a type of valve used to control the pressure in a system) to protect electrical systems from excess voltages.
Construction of avalanche diode
Avalanche diodes are generally made from silicon or other semiconductor materials. The construction of avalanche diode is similar to zener diode but the doping level in avalanche diode differs from zener diode.
Zener diodes are heavily doped. Therefore, the width of depletion region in zener diode is very thin. Because of this thin depletion layer or region, reverse breakdown occurs at lower voltages in zener diode.
On the other hand, avalanche diodes are lightly doped. Therefore, the width of depletion layer in avalanche diode is very wide compared to the zener diode. Because of this wide depletion region, reverse breakdown occurs at higher voltages in avalanche diode. The breakdown voltage of avalanche diode is carefully set by controlling the doping level during manufacture.
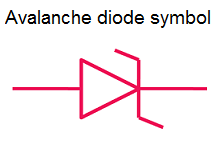
Symbol of avalanche diode
The symbol of avalanche and zener diode is same. Avalanche diode consists of two terminals: anode and cathode. The symbol of avalanche diode is shown in below figure.
The symbol of avalanche diode is similar to the normal diode but with the bend edges on the vertical bar.
How avalanche diode works?
A normal p-n junction diode allows electric current only in forward direction whereas an avalanche diode allows electric current in both forward and reverse directions. However, avalanche diode is specifically designed to operate in reverse biased condition.
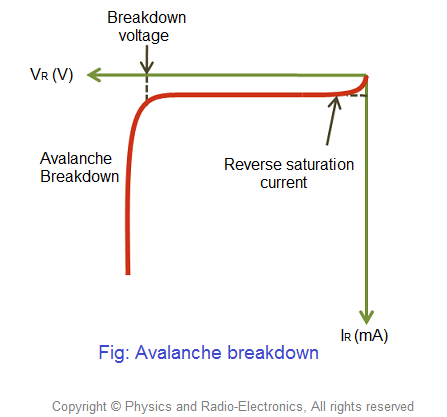
Avalanche diode allows electric current in reverse direction when reverse bias voltage exceeds the breakdown voltage. The point or voltage at which electric current increases suddenly is called breakdown voltage.
When the reverse bias voltage applied to the avalanche diode exceeds the breakdown voltage, a junction breakdown occurs. This junction breakdown is called avalanche breakdown.
When forward bias voltage is applied to the avalanche diode, it works like a normal p-n junction diode by allowing electric current through it.
When reverse bias voltage is applied to the avalanche diode, the free electrons (majority carriers) in the n-type semiconductor and the holes (majority carriers) in the p-type semiconductor are moved away from the junction. As a result, the width of depletion region increases. Therefore, the majority carriers will not carry electric current. However, the minority carriers (free electrons in p-type and holes in n-type) experience a repulsive force from external voltage.
As a result, the minority carriers flow from p-type to n-type and n-type to p-type by carrying the electric current. However, electric current carried by minority carriers is very small. This small electric current carried by minority carriers is called reverse leakage current.
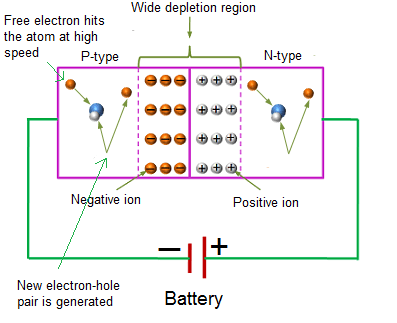
If the reverse bias voltage applied to the avalanche diode is further increased, the minority carriers (free electrons or holes) will gain large amount of energy and accelerated to greater velocities.
The free electrons moving at high speed will collide with the atoms and transfer their energy to the valence electrons.
The valance electrons which gains enough energy from the high-speed electrons will be detached from the parent atom and become free electrons. These free electrons are again accelerated. When these free electrons again collide with other atoms, they knock off more electrons.
Because of this continuous collision with the atoms, a large number of minority carriers (free electrons or holes) are generated. These large numbers of free electrons carry excess current in the diode.
When the reverse voltage applied to the avalanche diode continuously increases, at some point the junction breakdown or avalanche breakdown occurs. At this point, a small increase in voltage will suddenly increases the electric current. This sudden increase of electric current may permanently destroys the normal p-n junction diode. However, avalanche diodes may not be destroyed because they are carefully designed to operate in avalanche breakdown region.
The breakdown voltage of the avalanche diode depends on the doping density. Increasing the doping density will decreases the breakdown voltage of the avalanche diode.
Applications of avalanche diodes
- Avalanche diodes can be used as white noise generators.
- Avalanche diodes are used in protecting circuits.
Types of Diodes
The various types of diodes are as follows: