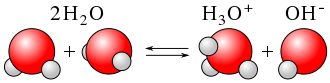
Ionization of the Water Molecule
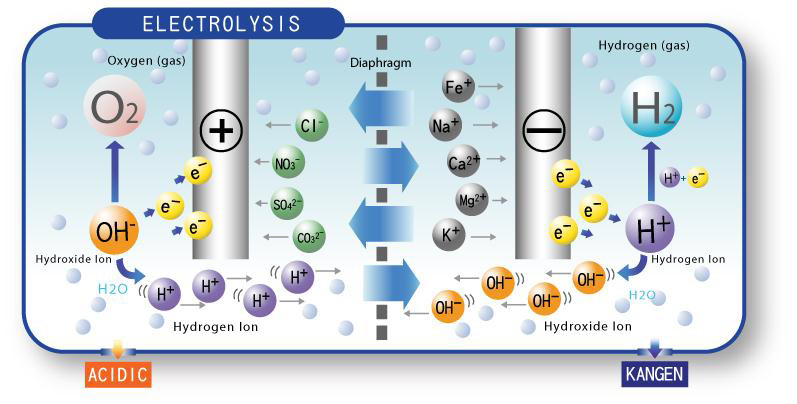
 In a tubular water-filled capacitor, water molecules are ionized due to the presence of an electric field between the two tubular plates. This ionization process is important in understanding the behavior of the capacitor, as it can lead to dielectric breakdown and other issues.
In a tubular water-filled capacitor, water molecules are ionized due to the presence of an electric field between the two tubular plates. This ionization process is important in understanding the behavior of the capacitor, as it can lead to dielectric breakdown and other issues.
When an electric field is applied to the water-filled capacitor, the water molecules become polarized, with the positive ends of the molecules orienting towards the negative plate and the negative ends orienting towards the positive plate. As the electric field increases, the polarization becomes stronger, and some of the water molecules are ionized, releasing H+ and OH- ions into the water.
Over-ionization can occur if the electric field becomes too strong, leading to the breakdown of the dielectric and the formation of a conducting path between the two plates. This can cause a sudden discharge of the stored energy in the capacitor, leading to damage or failure of the system. Dielectric breakdown can also occur if the water contains impurities or dissolved ions that can enhance the conductivity of the water and decrease the dielectric strength.
The ionization process in the water-filled capacitor leads to the formation of H+ and OH- ions in the water. The H+ ions are positively charged and are attracted towards the negative plate, while the OH- ions are negatively charged and are attracted towards the positive plate. This movement of ions in the water creates an electric current, which can affect the behavior of the capacitor and lead to issues such as self-discharge and leakage current.
The creation of H+ and OH- ions in the water-filled capacitor can also have other effects, such as affecting the pH of the water. As H+ ions are released into the water, the pH of the water becomes more acidic, while the release of OH- ions can make the water more basic. The pH of the water can affect the behavior of the capacitor, as changes in pH can alter the conductivity and dielectric properties of the water.
In conclusion, the ionization of water molecules in a tubular water-filled capacitor is an important process that can affect the behavior of the capacitor. Over-ionization can lead to dielectric breakdown, while the creation of H+ and OH- ions can affect the pH and conductivity of the water. Understanding these processes is important in designing and operating water-filled capacitors for various applications.