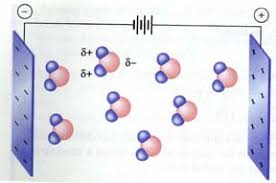
Polarization in a Water Capacitor
A capacitor is a device that stores electrical energy in an electric field by separating charges on two conductive plates that are separated by a non-conductive material called a dielectric. In the case of a water-filled capacitor with two tubular plates, the dielectric is the water itself. This type of capacitor is called an electrolytic capacitor, and it has some unique properties due to the polarization of the water molecule.
The water molecule is a polar molecule, meaning that it has a positive charge on one end and a negative charge on the other. This polarization is due to the unequal distribution of electrons in the molecule, which causes the oxygen atom to have a slight negative charge and the hydrogen atoms to have a slight positive charge. When a voltage is applied to the two tubular plates in the water-filled capacitor, the polar water molecules align themselves with the electric field, with the positive ends of the molecules facing the negative plate and the negative ends facing the positive plate. This causes a separation of charge in the water, with the positive ions accumulating near the negative plate and the negative ions near the positive plate.
The dielectric constant of a material is a measure of how easily it becomes polarized in an electric field. The dielectric constant of water is relatively high, which means that it is easily polarized by an applied electric field. This makes water a good dielectric material for use in electrolytic capacitors.
The 304L stainless tubing used in the water-filled capacitor is a good conductor of electricity, but it has a relatively low breakdown voltage. This means that if the voltage across the capacitor exceeds a certain threshold, the tubing can break down and become damaged. To increase the voltage threshold of the capacitor, the tubing can be doped with Cr2O3, which is a ceramic material that has a high dielectric strength. When the tubing is doped with Cr2O3, it becomes a better insulator and can withstand higher voltages without breaking down.
In summary, the electrical polarization of the water molecule in a water-filled capacitor with two tubular plates is an important factor in the capacitor's performance. The high dielectric constant of water allows for efficient energy storage, while the use of Cr2O3-doped 304L stainless tubing can increase the voltage threshold of the capacitor and prevent damage due to breakdown.