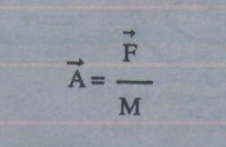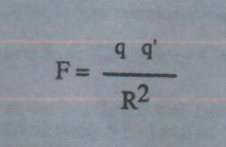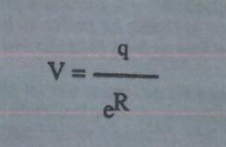Voltage Performs Work
Unlike voltage charges within an electrical circuit set up an “electrical attraction force”; in both cases, electrical charges within the same electrical circuit generates an repelling action.
Electrical forces are known as “voltage fields” and can exhibit either a positive or negative electrical charge.
Likewise, Ions or Particles within the electrical circuit having unlike electrical charges are attracted to each other. Ions or particles mass having the same or like electrical charges will move away from one another, as illustrated in Figure 1-3.
Furthermore, electrical charged ions or particles can move toward stationary voltage fields of opposite polarity, and, is given by Newton's second law
Where
The acceleration (A⃗) of an particle mass (M) acted on by a Net Force (F⃗).
Whereby
Net Force (F⃗) is the “electrical attraction force” between opposite electrically charged entities, and, is given by Coulomb’s Law
Whereas
Difference of potential between two charges is measured by the work necessary to bring the charges together, and, is given by
The potential at a point due to a charge (q) at a distance (R) in a medium whose dielectric constant is (e).