Capacitance Reactance
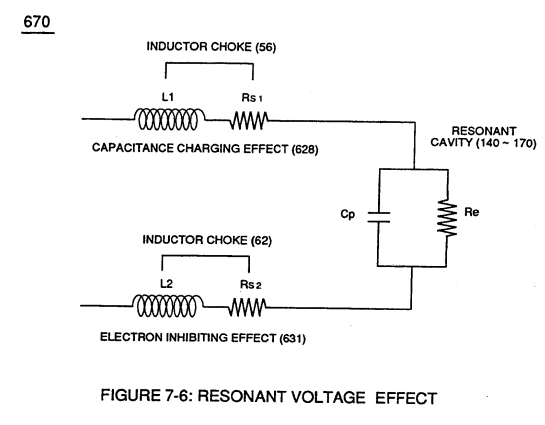
Capacitance Reactance is determined by the insulation resistance (Rs+Re) and Inductance (L1/L2) interacting together during D.C. Pulsing.
Dielectric property of water opposes amp leakage (Re) while another property of water takes-on an "Electrical Charge".
Water temperature (Rt) (cool-to-the-touch) keeps (Re) constant since amp flow remains minimal.
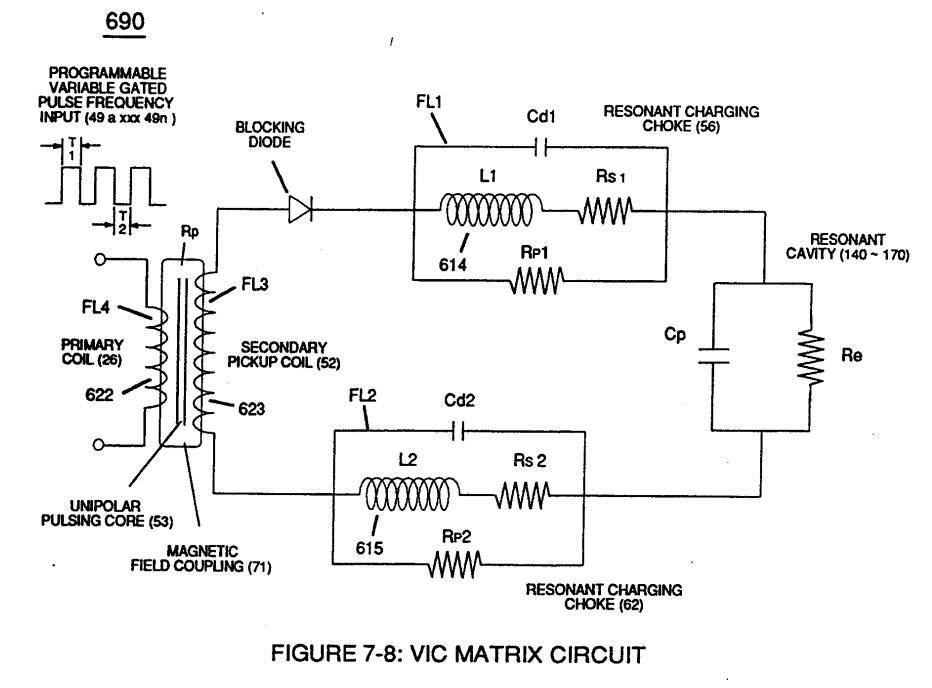
Plate Inductance (Lc) is Inductance Reactance of Inductor (L1 ) and Inductance Reactance of Inductor (L2) in series with Resonant Capacitor (140 -170) of Figure (7-6) as to (690) of Figure (7-8).
|
Resonant Capacitor (140 -170) of Figure (7-6) |
(690) of Figure (7-8) |
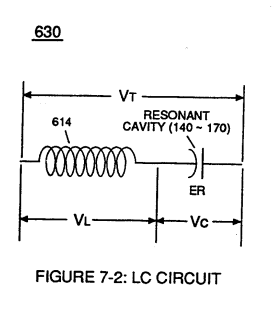
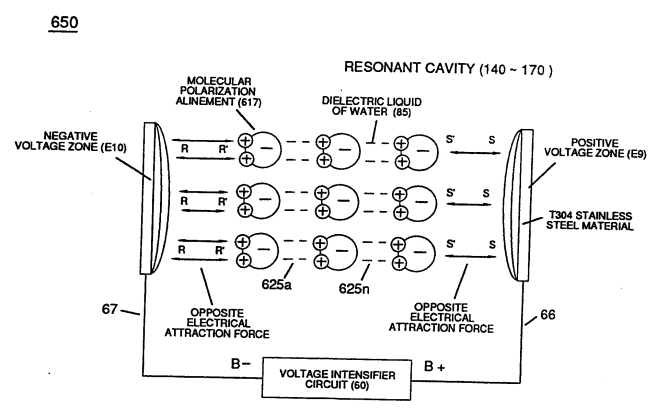
In terms of Component Reactance, Inductors (L1/L2) should always be larger than Capacitor (ER) of Figure (7-2) in order to maximize amp restriction to enhance "Voltage Deflection" (SS' - 617a xxx 617n - RR') of Figure (7-4) and, is expressed by :
|
Capacitor (ER) of Figure (7-2) |
"Voltage Deflection" of Figure (7-4) |
Whereas,
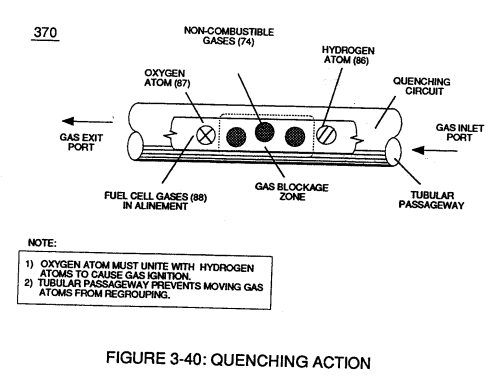
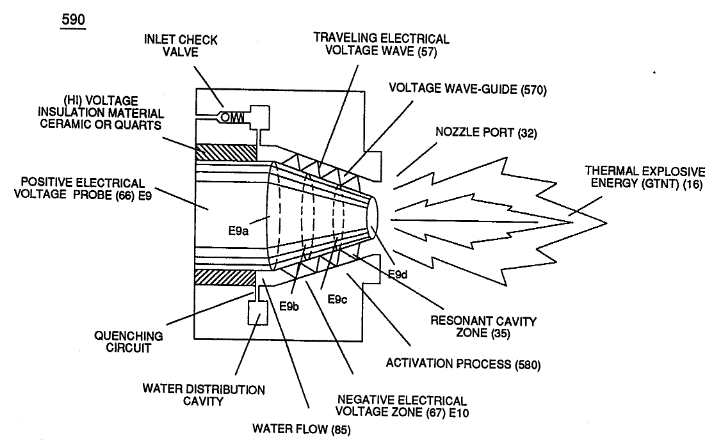
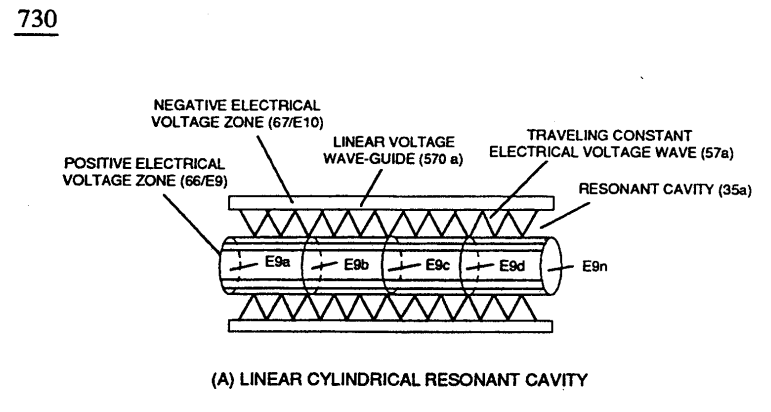
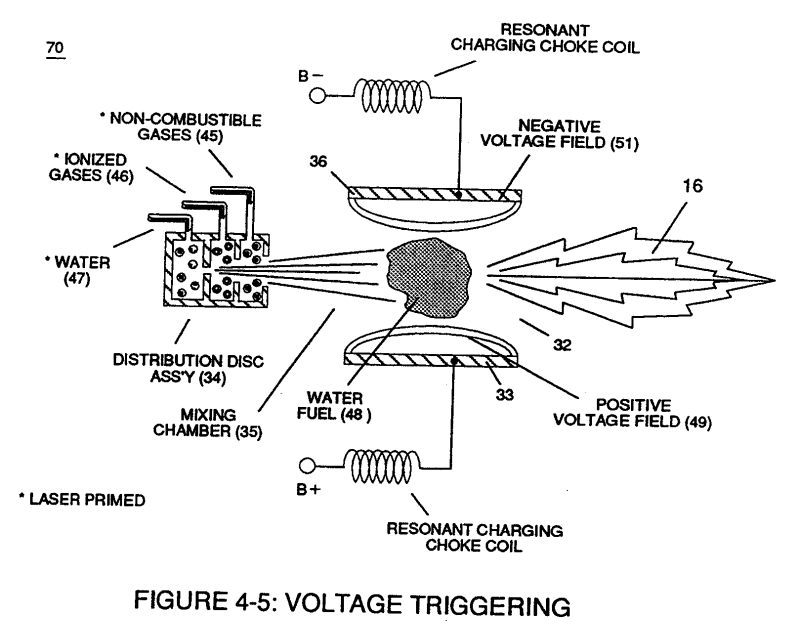
Capacitor (ER) should remain relatively small due to the dielectric value of water to obtain maximum Thermal Explosive Energy-Yield (16a xxx 16n) of Figure (4-5) and subsequently establishing Quenching Circuit (370) of Figure (3-40) to prevent gas ignition inside traveling voltage wave-guide (590) of Figure (6-2) as to (730) of Figure (7-12)
|
Quenching Circuit (370) of Figure (3-40) |
(590) of Figure (6-2) |
(730) of Figure (7-12) |
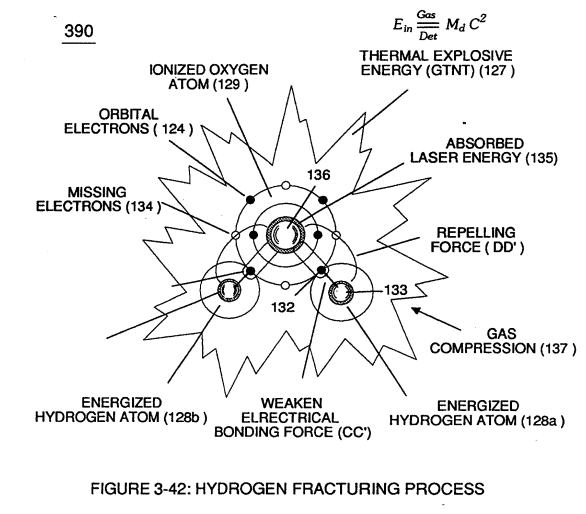
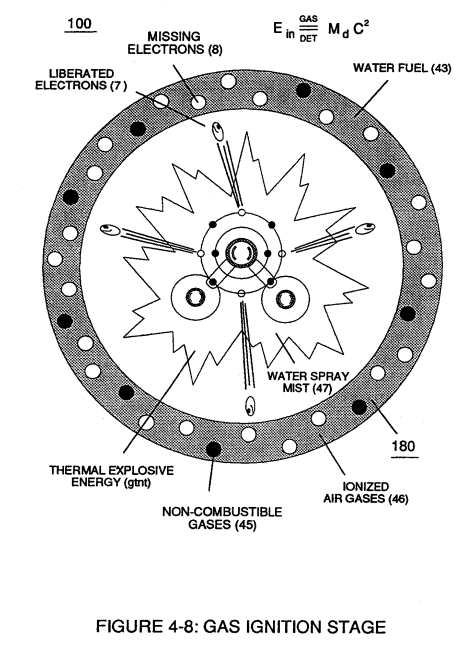
... to bring-on and trigger Hydrogen Fracturing Process (390) of Figure (3-42) once liberated and expanding water gases (100) of Figure (4-8) passes beyond exit port (E9d)
|
(390) of Figure (3-42) |
(100) of Figure (4-8) |
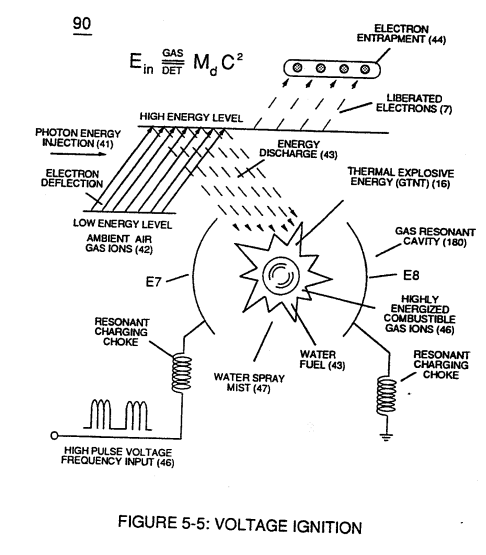
... activating Voltage Ignition Process (90) of Figure (5-5)
|
(90) of Figure (5-5) |
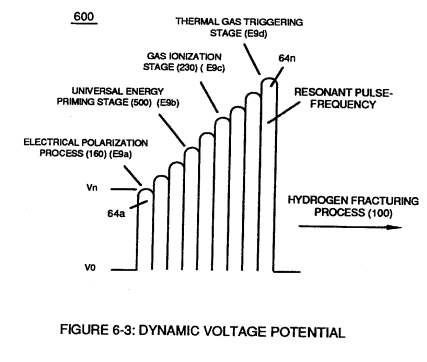
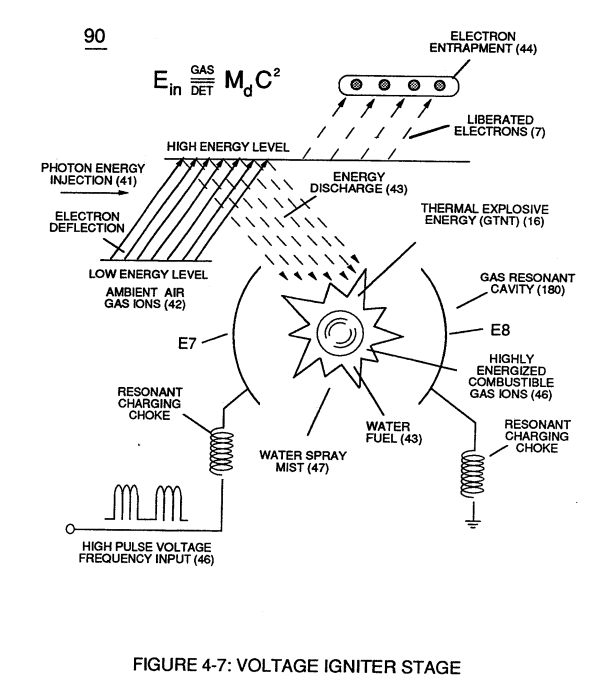
... utilizing Dynamic Voltage Potential (600) of Figure (6-3) of opposite electrical stress (SS' - 617 - RR') to cause thermal atomic agitation (90) of Figure (4-7) (kinetic heat by atomic motion)
|
(600) of Figure (6-3) |
(90) of Figure (4-7) |
which, when occurring at gas exit port (32) of Figure (4-5), spark-ignites expanding water gas-fuel (45/46/47) of Figure (4-5) during water inject cycle (70) of Figure (4-5)
|
Figure (4-5) |
... releasing thermal explosive energy (gtnt) (16) under control state.